How Long Is Law School in the US? Timeline Explained
If you're researching how long is law school, you've probably encountered conflicting information online—claims that duration varies by state, rumors that elite schools require extra years, or confusion about whether law school includes undergraduate education. The reality is much simpler: US law school follows a highly structured, predictable timeline regulated by the American Bar Association (ABA).
This comprehensive guide will explain exactly how long law school takes in the United States, clarify the timeline after earning your bachelor's degree, compare full-time and part-time programs, examine duration at prestigious institutions like Harvard and Yale, and address state-specific questions. Whether you're planning your legal education path or simply curious about the commitment required, you'll find clear, accurate answers here. Let's break down the complete law school timeline with no confusion or unnecessary complexity.
Standard US Law School Timeline
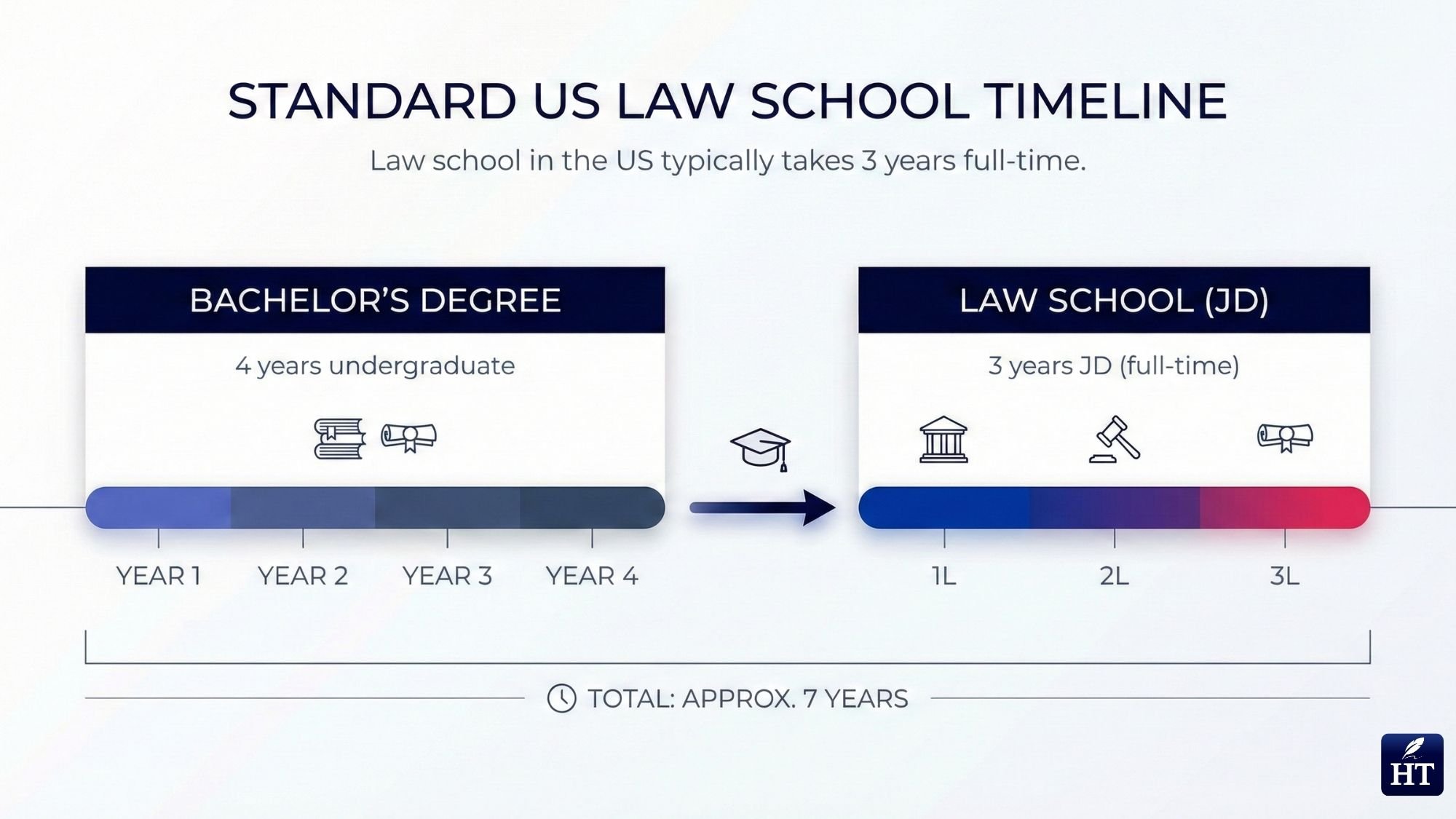
Law school in the United States typically takes 3 years to complete if attended full-time. Part-time or evening law school programs usually take 4 years. Law school begins after earning a bachelor's degree and follows the same timeline across most ABA-accredited law schools in the US.
How Long Is Law School in the US?
Law school in the United States follows a standardized structure regulated by the American Bar Association (ABA), which accredits nearly all law schools nationwide. The Juris Doctor (JD) degree—the primary credential required to practice law in the US—has a consistent duration regardless of which law school you attend or where it's located.
Understanding how long law school takes requires recognizing that legal education in America is a post-graduate program. Unlike medical school or other professional programs with variable timelines, law school maintains remarkable consistency across institutions. This standardization ensures that graduates from any ABA-accredited school receive equivalent foundational legal training.
The standard answer: 3 years full-time or 4 years part-time. This timeline applies whether you're attending a public state university law school or an Ivy League institution. The curriculum is designed to build progressively across three academic years, with each year serving a specific purpose in your legal education.
Let's examine how this timeline breaks down year by year, what happens after your bachelor's degree, and when alternative pathways might extend or compress this schedule.
Standard Law School Length (Full-Time JD Programs)
Most students attend law school full-time and complete their Juris Doctor (JD) in three academic years. This is the traditional path and what people mean when they reference "law school" without additional qualifiers.
How the three years progress:
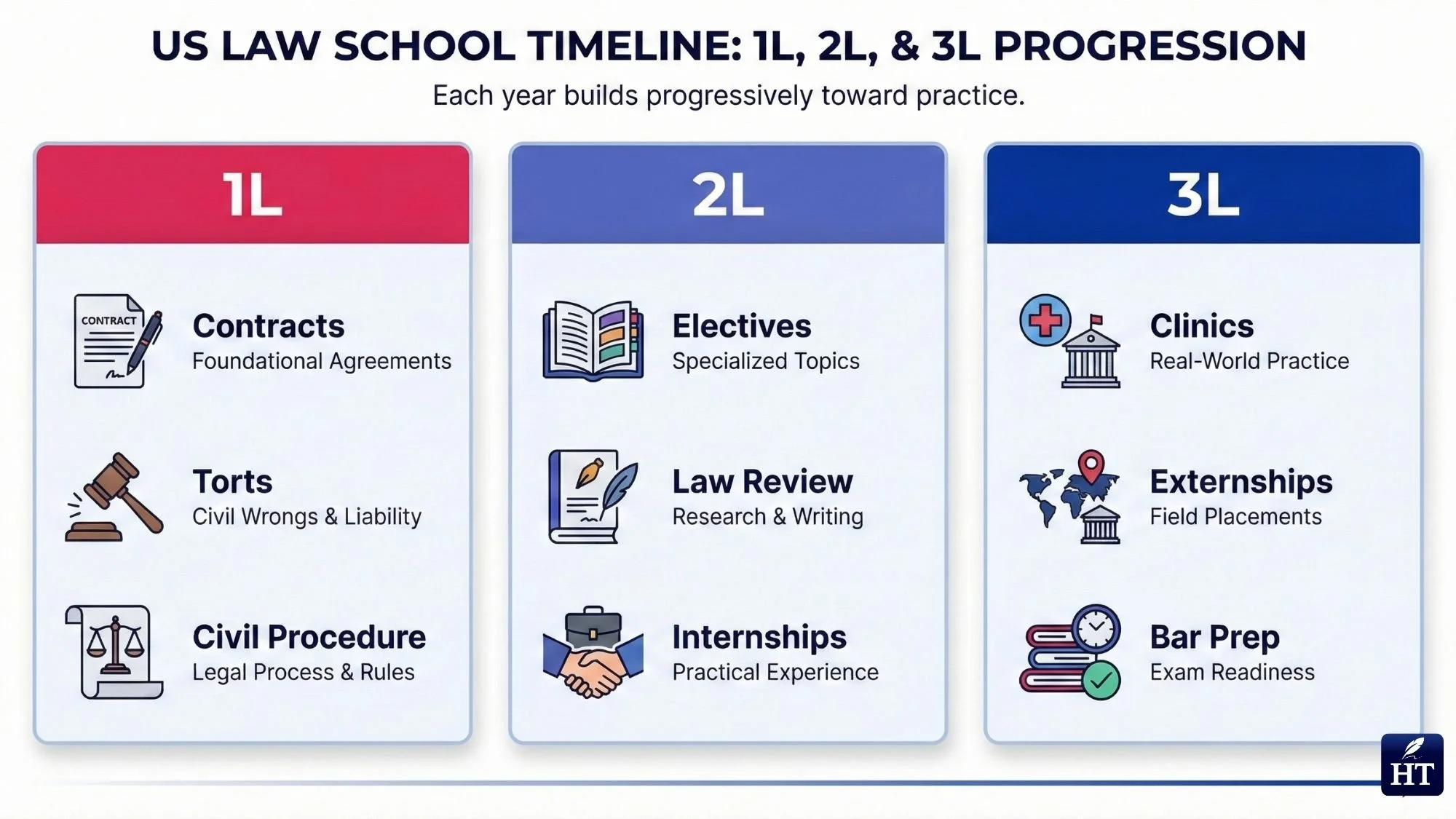
Year 1 (1L) - Building Foundations: Your first year focuses entirely on core legal subjects required by all law students. You'll study contracts, torts, civil procedure, constitutional law, property law, and legal research and writing. The 1L year is highly structured with little room for electives, ensuring every law student masters fundamental legal reasoning and analysis. This year is typically the most academically intense as you adjust to the Socratic method of teaching and learn to "think like a lawyer."
Year 2 (2L) - Exploring Specializations: The second year opens up significantly, allowing you to choose electives based on your interests—criminal law, corporate law, environmental law, intellectual property, and dozens of other specializations. Many students participate in moot court competitions, join law review or other journals, and secure summer internships or clerkships. This year helps you identify which area of law you want to practice.
Year 3 (3L) - Practical Application: Your final year emphasizes clinical experience, advanced seminars, and bar exam preparation. Many students complete externships with judges, prosecutors, public defenders, or law firms. Some schools offer specialized clinics where you work on real cases under supervision. By graduation, you've transitioned from learning theory to applying legal knowledge practically.
Standard full-time JD program structure:
Total duration: 3 academic years (typically September to May)
Year 1 (1L): Foundational legal subjects, mandatory curriculum
Year 2 (2L): Electives, internships, law review, specialization exploration
Year 3 (3L): Clinics, advanced seminars, bar preparation, job search
How Long Is Law School After a Bachelor's Degree?
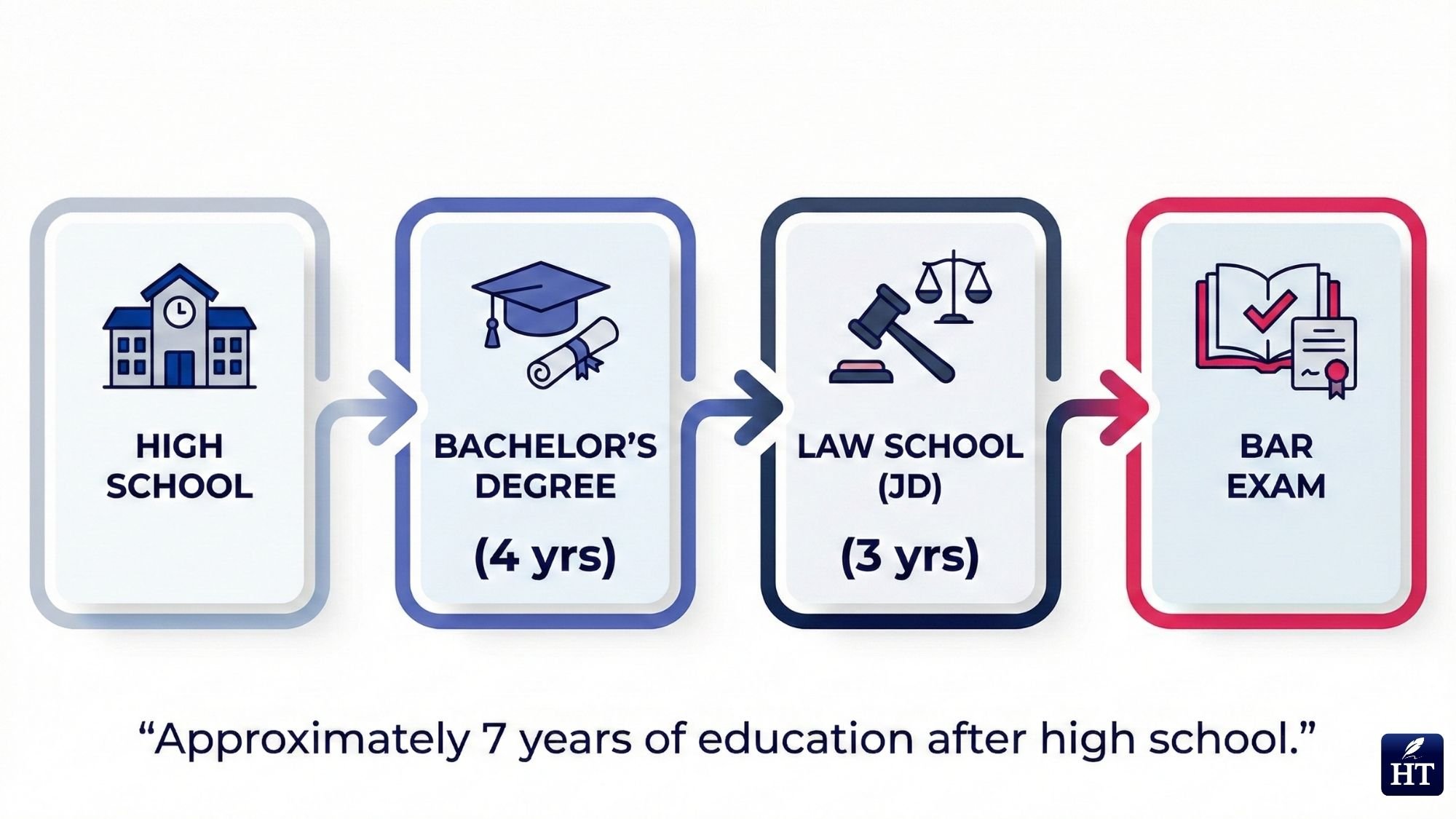
Law school is a graduate program, not an undergraduate degree. This distinction is crucial because it clarifies the total educational timeline required to become a lawyer in the United States.
You cannot attend law school directly after high school. First, you must complete a four-year bachelor's degree in any major (law schools accept students from all undergraduate disciplines—English, political science, engineering, biology, business, etc.). Only after earning your bachelor's degree and taking the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) or an accepted alternative can you apply to law school.
Complete educational timeline from high school to law degree:
Bachelor's degree: Typically 4 years of undergraduate education
Law school (JD): 3 additional years of graduate study
Total education timeline: Approximately 7 years after high school
LSAT or equivalent exam: Required before law school admission (taken during senior year of college or during a gap year)
Important clarification: When someone asks "how long is law school after college," the answer is 3 years. When asking "how long does it take to become a lawyer," you must include both undergraduate (4 years) and law school (3 years), plus bar exam preparation.
How Long Is Part-Time Law School?
Part-time law school programs are designed for working professionals, parents, career switchers, or anyone who cannot commit to full-time daytime study. These programs offer the exact same JD degree and legal education—only the pace and schedule differ.
Part-time programs typically take 4 years to complete instead of 3, allowing students to balance their legal education with employment, family responsibilities, or other commitments. Classes usually meet during evenings (after 6 PM) or on weekends, though schedules vary by institution.
Key characteristics of part-time law school:
Typical duration: 4 years (some programs offer 4.5-year options)
Evening or weekend classes: Scheduled outside traditional work hours
Same JD credential: Identical degree and bar eligibility as full-time programs
Common in major cities and public universities: Urban law schools often serve working populations
Reduced course load per semester: Fewer classes each term spread over more years
Flexibility: Some schools allow switching between part-time and full-time status
Important consideration: Part-time students are eligible for the same bar exam and practice the same law as full-time graduates. The credential is identical, though networking opportunities and access to certain competitive summer programs may differ due to scheduling.
Is There a Faster Way to Finish Law School?
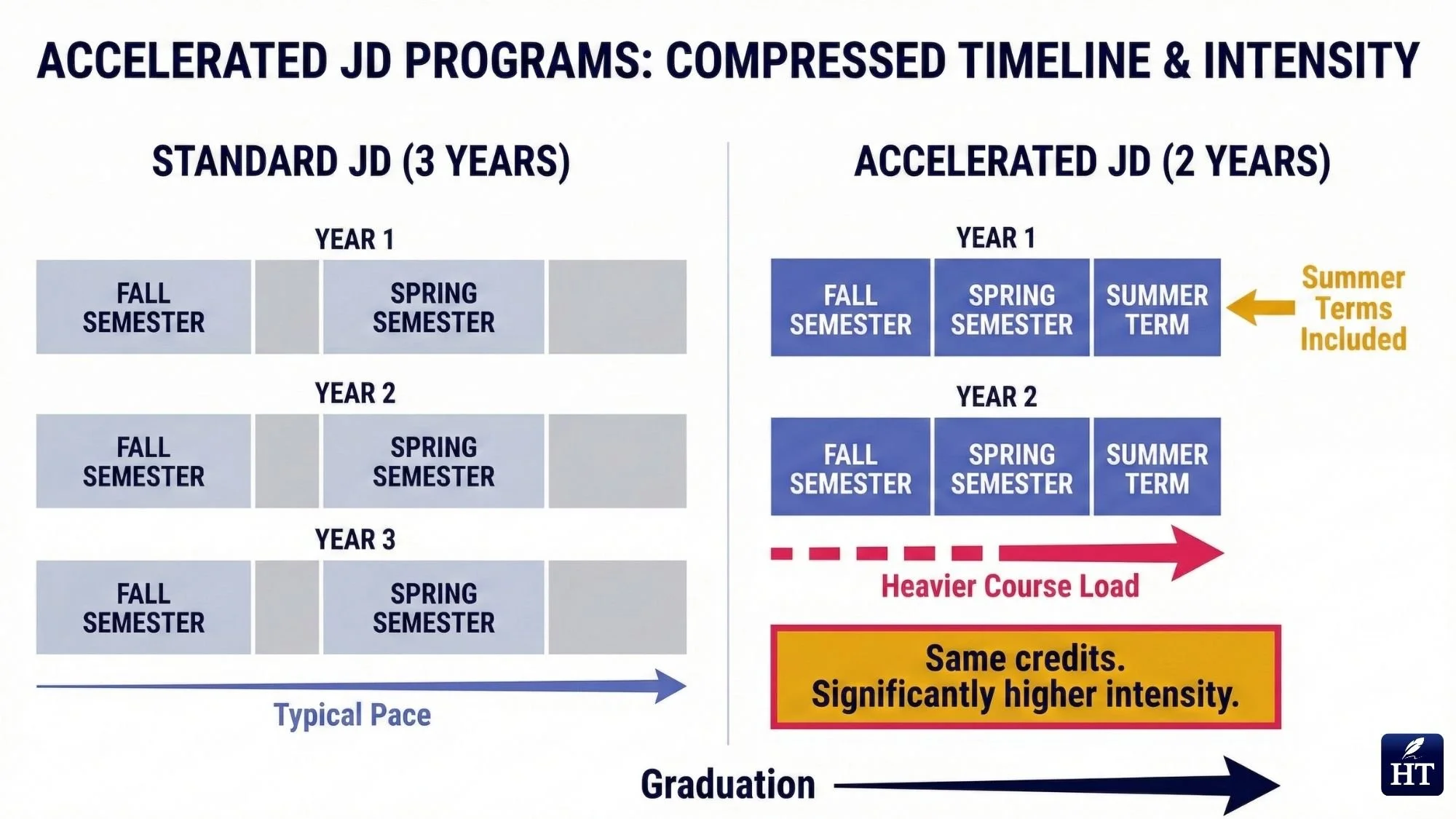
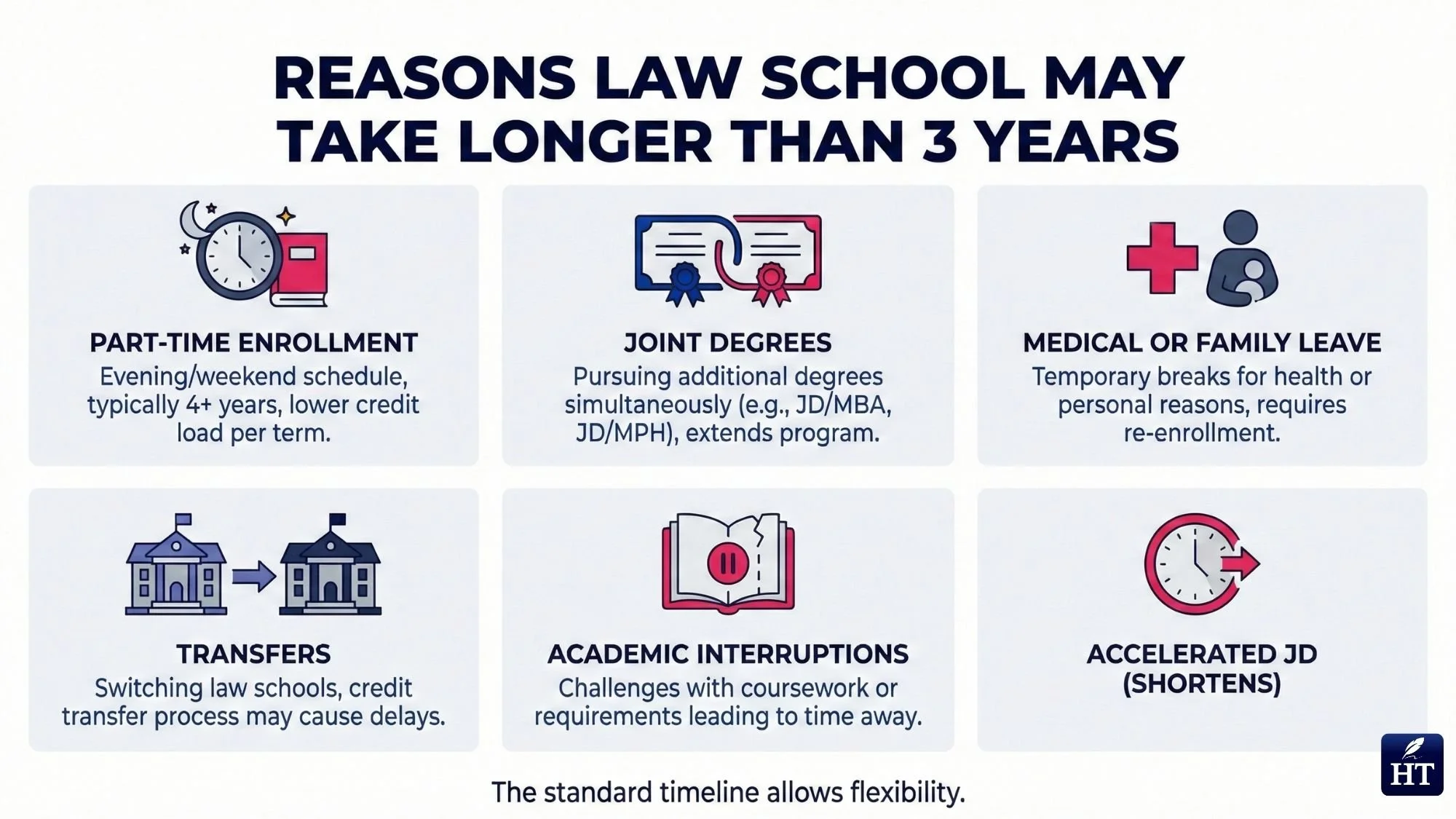
Accelerated JD programs exist but are uncommon and extremely demanding. A small number of law schools offer accelerated tracks that compress the standard three-year curriculum into approximately two years through year-round study.
How accelerated programs work:
These programs require students to attend classes during summer semesters in addition to fall and spring terms, maintaining a heavier course load throughout. Students complete the same total credit hours and curriculum requirements as traditional three-year programs—the compression comes from eliminating breaks, not reducing content.
Characteristics of accelerated law programs:
Accelerated JD programs: Approximately 2 to 2.5 years
Includes summer semesters: Year-round attendance with minimal breaks
Heavier course load: More classes per semester than traditional programs
Must still meet ABA requirements: Same total credits and curricular standards
Limited availability: Only offered at select law schools
Intense commitment: Little time for internships, part-time work, or extracurriculars
Trade-offs to consider:
While accelerated programs save time and tuition costs, they offer fewer opportunities for summer internships and clerkships that provide valuable experience and job prospects. Many legal employers expect to see summer work experience on resumes, which accelerated students have less time to accumulate.
Examples of schools offering accelerated options: Northwestern University Pritzker School of Law offers a two-year JD program, and a few other institutions have pilot programs. However, the vast majority of law schools maintain only the traditional three-year track.
How Long Is Law School at Top US Universities?
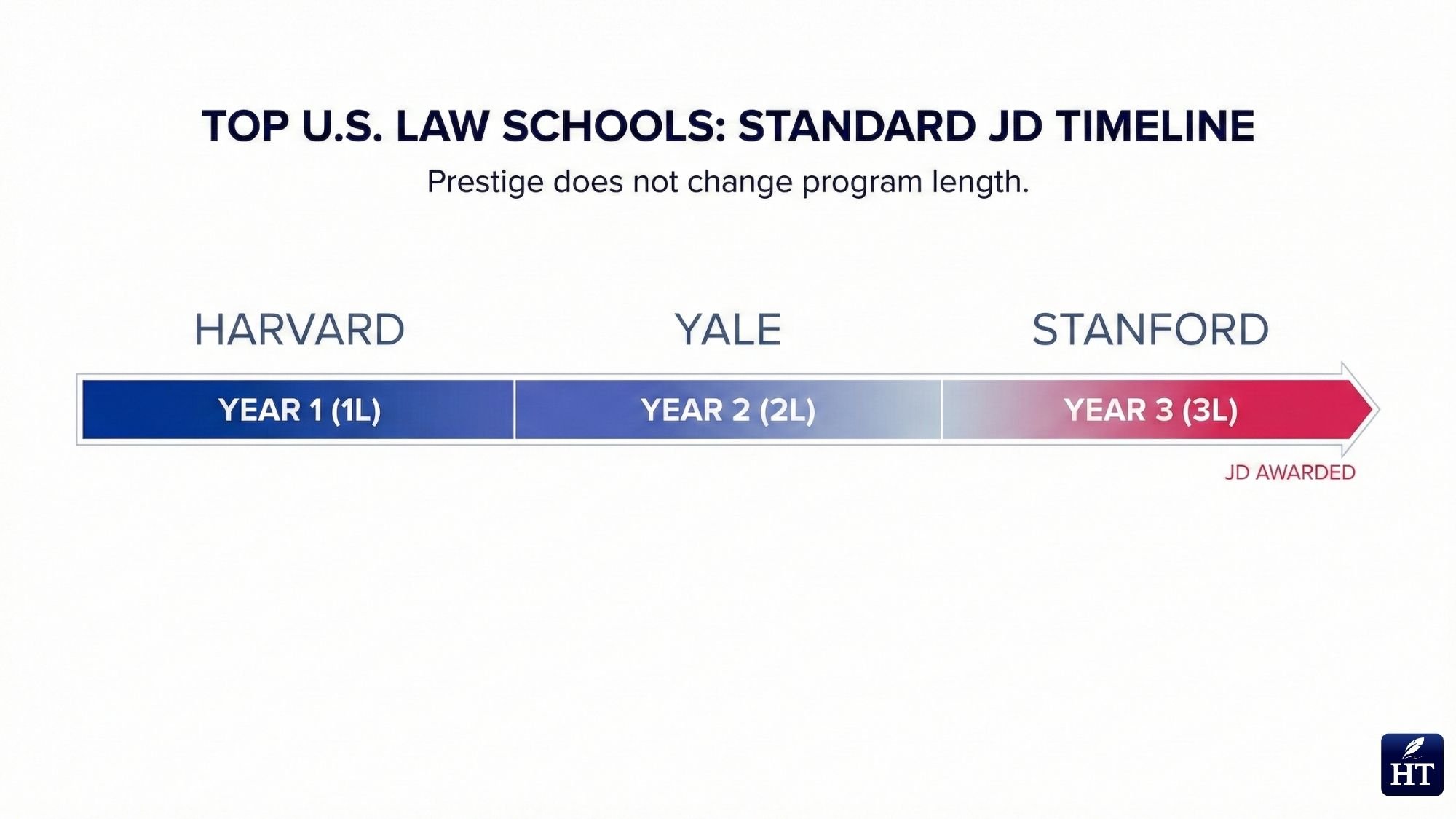
A common misconception is that prestigious law schools require more years of study. This is false. Elite institutions like Harvard, Yale, Stanford, Columbia, and other top-ranked law schools all follow the same three-year JD timeline as every other ABA-accredited program in the United States.
Why the confusion exists:
Prospective students sometimes assume that schools with more rigorous academics, smaller class sizes, or higher bar passage rates must have longer programs. In reality, the difference lies in admissions selectivity, teaching quality, resources, and career outcomes—not duration.
The truth: All ABA-accredited law schools, regardless of ranking or prestige, must meet the same structural requirements for the JD degree, including a minimum number of credit hours completed over a minimum time period. This creates uniformity in program length across institutions.
How Long Is Harvard Law School?
Harvard Law School follows the standard US JD structure of 3 years for full-time students. Despite being one of the world's most prestigious law schools with highly competitive admissions (typically accepting under 15% of applicants), Harvard does not extend the basic JD timeline.
Harvard Law School JD timeline:
Full-time JD: 3 years (no exceptions for standard JD track)
No shortened JD track: Harvard does not offer accelerated two-year programs
Joint degrees may extend total time: JD/MBA, JD/MPP, and other combined programs add 1-2 years but are separate from the core JD
What makes Harvard different isn't duration but rather the depth of resources, faculty expertise, extensive clinical opportunities, and career placement outcomes. Students complete the same three-year journey as peers at other law schools, just with access to different opportunities and networks during those years.
How Long Is Law School at Yale?
Yale Law School, consistently ranked #1 in US News rankings, also requires 3 years for its full-time JD program.Yale's reputation for academic excellence and small class sizes (roughly 200 students per class) doesn't translate to additional years of study.
Yale Law School JD timeline:
Full-time JD: 3 years (standard program)
Research-focused curriculum: Emphasizes legal theory and scholarship alongside practical training
Same ABA standards as other US schools: Must meet identical accreditation requirements
Optional extended programs: Students can petition for reduced course loads in specific circumstances, extending time slightly, but this is rare
Yale's distinction comes from its academic approach (more flexible curriculum, less emphasis on grades, stronger focus on public interest law) rather than program length. Graduates complete the same total credits over the same three-year period as students at any other accredited law school.
Bottom line for elite schools: Whether you attend Harvard, Yale, Stanford, Columbia, University of Chicago, NYU, or any other top-ranked institution, you'll spend 3 years earning your JD if attending full-time.
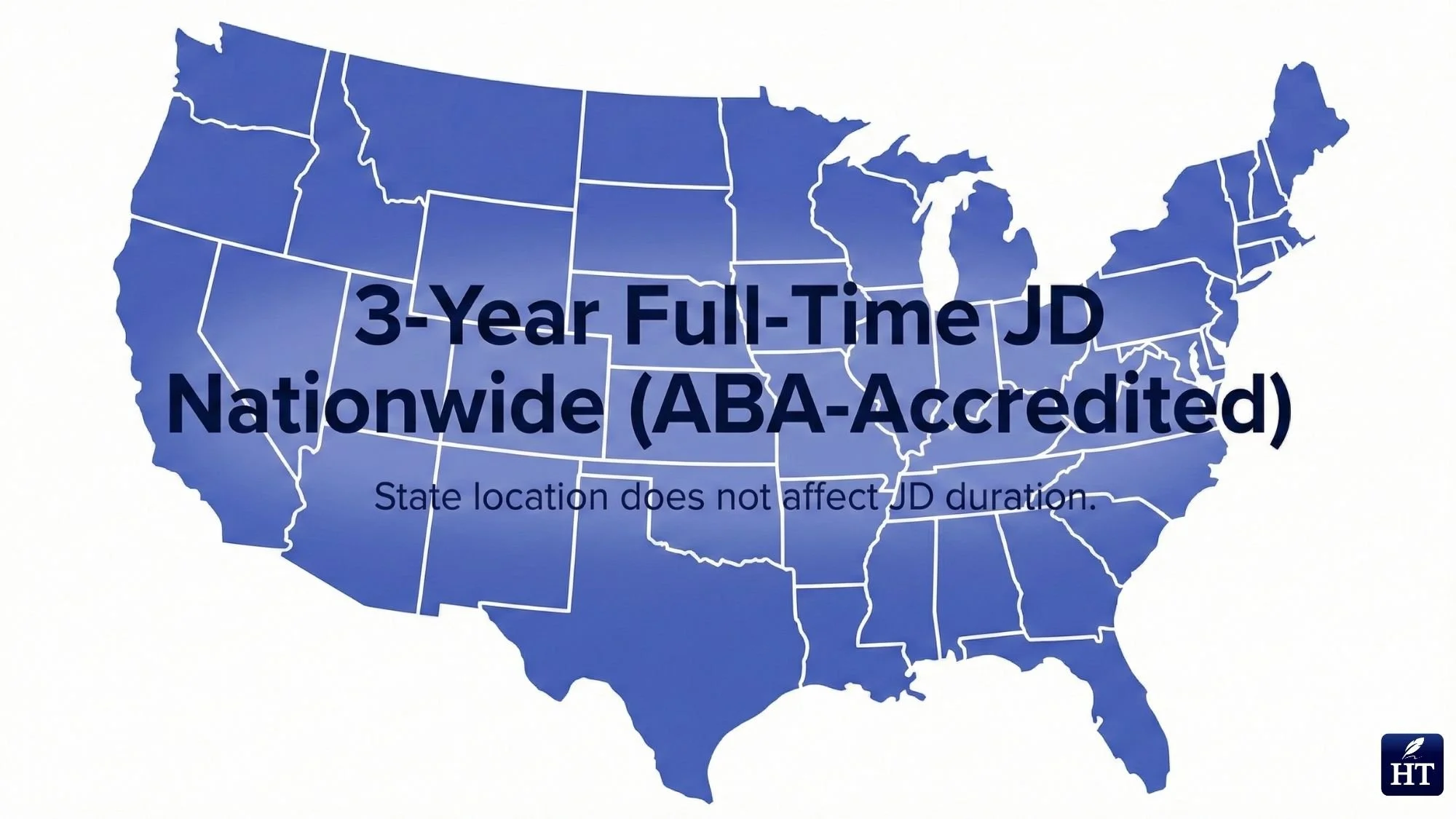
How Long Is Law School by State?
A critical clarification: State location does not change law school length. The duration of JD programs is standardized by ABA accreditation requirements, not by individual state regulations. Whether you attend law school in California, Texas, New York, Florida, or any other state, the timeline remains consistent.
Where state differences DO matter:
Bar exam requirements: Each state sets its own bar exam content and passing standards
Admission prerequisites: Some states have specific requirements for practicing law
Reciprocity rules: Transferring your law license between states varies
Apprenticeship programs: California and a few other states offer alternative paths to bar admission without attending law school (these are rare and very different from traditional JD programs)
But JD program duration? Always 3 years full-time, 4 years part-time, regardless of state.
California, Texas, New York
These three states host the largest legal markets in the US and are frequently searched, leading to questions about whether law school takes longer there. The answer: No—all three states follow standard timelines.
Law school duration in major legal markets:
California: 3 years full-time for JD programs at all ABA-accredited schools
Texas: 3 years full-time (University of Texas, SMU, Baylor, etc.)
New York: 3 years full-time (Columbia, NYU, Fordham, Cornell, etc.)
Part-time options available: All three states have schools offering 4-year evening programs
California's unique distinction: California allows "reading the law" (apprenticeship with a practicing attorney) as an alternative to law school, but this is extremely uncommon and takes at least 4 years with a much lower bar passage rate than traditional law schools.
Florida, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Ohio
Smaller-volume legal markets follow identical standards. Students in these states attend law school for the same duration as students anywhere else in the US.
Law school timeline in these states:
Standard JD length: 3 years full-time at all ABA-accredited programs
ABA-accredited programs: Schools must meet national standards regardless of location
Evening/part-time options vary by school: Some institutions offer 4-year programs, others don't
Examples: University of Florida (3 years), Rutgers Law (3 years), University of Pennsylvania Law (3 years), Ohio State Moritz College of Law (3 years)
State-specific considerations affect bar admission requirements and reciprocity, but not the core JD timeline. A University of Florida law student completes their degree in the same time frame as a Stanford law student
Factors That Can Change How Long Law School Takes
While the standard JD program is 3 years full-time, several factors can extend your timeline. Understanding these variables helps you plan realistically for your legal education journey.
Common factors that extend law school duration:
Part-time enrollment: Choosing evening or weekend programs extends completion to 4 years
Dual degree programs (JD/MBA, JD/PhD, JD/MPP): Combined programs typically add 1-2 years to your education, resulting in 4-5 total years
Academic interruptions: Medical leave, family emergencies, or financial difficulties may require taking time off
Transfers between schools: Changing law schools can sometimes extend graduation if credits don't transfer perfectly
Personal circumstances: Military deployment, childbirth, elder care, or other life events may necessitate reduced course loads
Academic performance: Students who fail courses or don't meet progression standards may need additional semesters
Gap years: Taking time between 1L and 2L or 2L and 3L (less common but permitted at some schools)
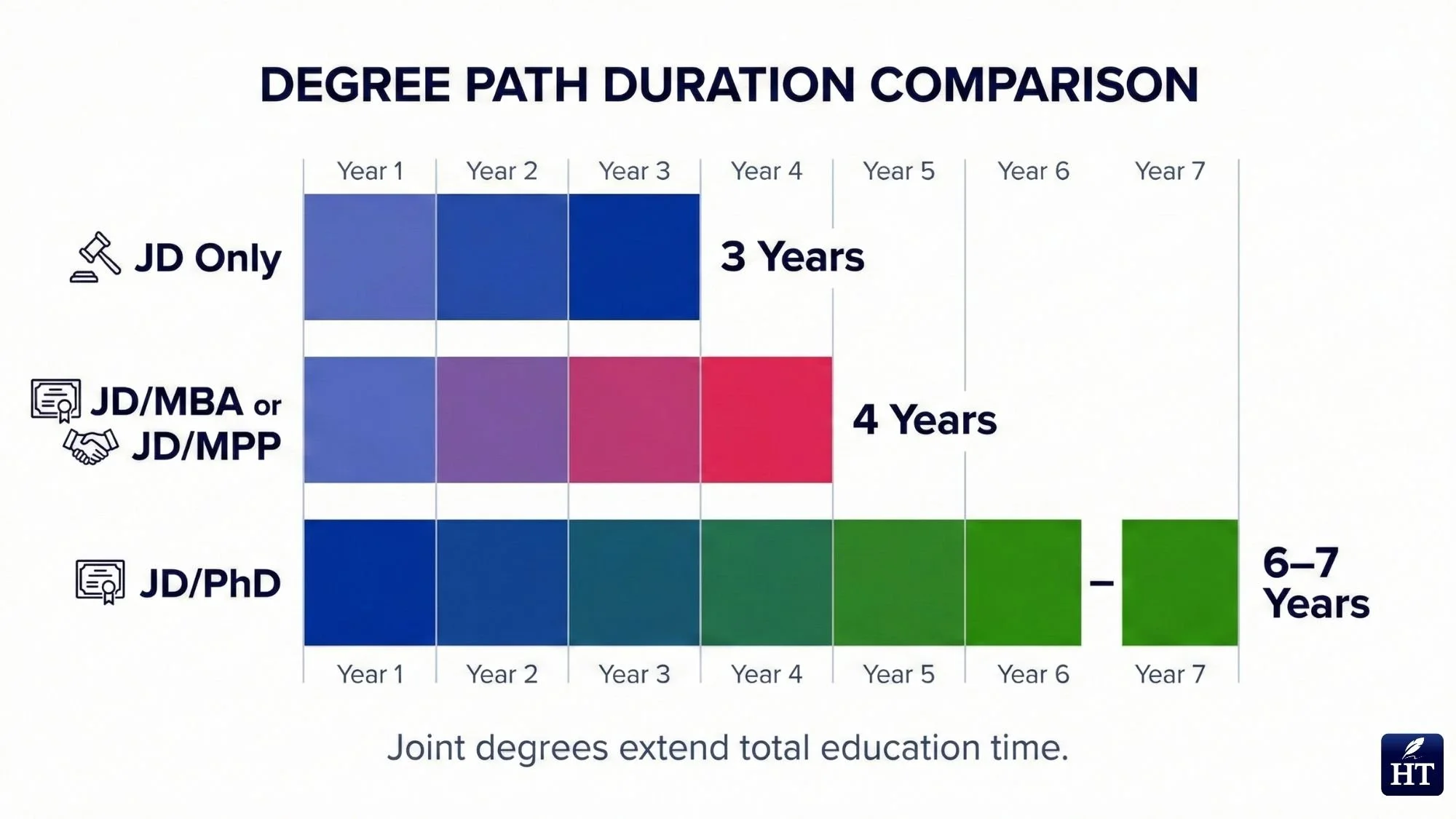
Dual degree programs explained:
Many law schools offer joint degree programs that result in two credentials. Common combinations include:
JD/MBA: 4 years (saves 1 year compared to earning both separately)
JD/MPP or JD/MPA: 4 years (public policy focus)
JD/PhD: 6-7 years (research-intensive path)
These programs are structured to allow some overlapping coursework, reducing total time compared to completing both degrees sequentially.
Planning tip: If you anticipate needing flexibility due to work or family obligations, research part-time programs or schools with flexible attendance policies before enrolling. Most schools discourage switching from full-time to part-time mid-program.
FAQs — How Long Is Law School?
How long is law school in the US?
Law school in the United States takes 3 years to complete if you attend full-time at an ABA-accredited institution. This timeline is standard across nearly all law schools nationwide, regardless of ranking, location, or prestige. Part-time evening or weekend programs extend the duration to 4 years while offering the same JD degree.
How long is law school after college?
Law school takes 3 additional years after you complete your bachelor's degree. You must first earn a four-year undergraduate degree in any major before applying to law school. Combined with your bachelor's degree, the total educational timeline from high school graduation to earning your JD is approximately 7 years.
Is law school 3 or 4 years?
Law school is 3 years for full-time students and 4 years for part-time students. The vast majority of law students attend full-time daytime programs that take 3 academic years to complete. Part-time evening or weekend programs accommodate working professionals and take 4 years. Both paths result in the same JD credential.
How long is part-time law school?
Part-time law school typically takes 4 years to complete. These programs offer evening or weekend classes designed for students who work full-time or have other commitments. The curriculum and degree are identical to full-time programs—only the pace and schedule differ. Some schools offer 4.5-year part-time options for maximum flexibility.
Can you finish law school in 2 years?
Yes, but accelerated two-year JD programs are rare and extremely demanding. Only a handful of law schools offer these programs, which require year-round attendance including summers with no breaks. Students complete the same total credits and curriculum as three-year programs but at an intensified pace with limited time for internships or extracurricular activities.
How long is law school including undergrad?
Law school including undergraduate education takes approximately 7 years total after high school. This includes a 4-year bachelor's degree in any major followed by 3 years of full-time law school. If you attend part-time law school, the total timeline extends to 8 years. This does not include bar exam preparation time.
Does law school length vary by state?
No, law school length does not vary by state. All ABA-accredited law schools must meet the same national standards regardless of location, resulting in a uniform 3-year full-time JD program across all 50 states. State differences affect bar exam requirements and admission rules, not JD program duration.
Conclusion
Understanding how long is law school is straightforward once you cut through common misconceptions: 3 years full-time or 4 years part-time, regardless of which state you study in or whether you attend Harvard or your local state university. This standardized timeline ensures consistent legal education across the United States while providing flexibility through part-time options for those who need them.
Whether you're planning your path to becoming a lawyer or simply curious about the commitment required, remember that law school is a post-graduate program following your bachelor's degree. The total journey from high school graduation to practicing law takes approximately 7 years of education plus bar exam preparation and passage.
Ready to explore more education pathways and career timelines? Visit HYE Tutors for comprehensive guides on undergraduate degree timelines, graduate school programs, professional certifications, and career planning strategiesdesigned to help you make informed decisions about your future.
References:
American Bar Association: Law School Standards – Official ABA accreditation requirements
Harvard Law School: JD Program – Harvard's official program information
Yale Law School: Curriculum – Yale's official JD structure
Law School Admission Council – Official resource for prospective law students